
These days there are dozens of good choices for desktop 3D printers, but there’s one huge question to be asked first: do you want a resin or a filament 3D printer?
Today we find dozens of each style available at very good prices, some even as low as US$100. With few exceptions, the price of SLS or SLM 3D printing has mostly not yet to dropped into professional price ranges, so users are left with the choice of resin or filament.
Sometimes the choice is straightforward, as you might have a specific application in mind that effectively determines the choice of machine. However, it may not always be so clear.
Each machine type has advantages and disadvantages. Each machine has some requirements that may tip the choice in one direction or another.
Let’s take a look at these two types of 3D printers and see how they might play out in your scenario.
Filament 3D Printers
These machines are the oldest among the desktop fleet, but have advanced significantly in recent years to provide outstanding performance and material choice.
Filament 3D Printer Advantages
Material choice: There is a much wider choice of materials for filament 3D printers, and today that includes many functional materials used in engineering.
High-temperature potential: It is possible, with the correct 3D printer equipment, to 3D print high-temperature materials like PEEK or ULTEM.
Carbon fiber potential: Extremely strong materials, such as carbon fiber-infused filament, can be used.
Price: The price of some filament 3D printers can be quite low, but those provide only very basic capabilities.
Public support: Certain filament 3D printers have huge followings, and thus there are massive communities where one can gain support or perform research.
Large build volume: Print volumes can be quite large with filament machines, even up to 500mm on reasonably priced equipment. Much larger volumes can be had if you’re willing to pay even more.
Recyclable materials: Since the materials are thermoplastics, it is possible to recycle waste 3D prints or purchase new filament made from recycled material.
Filament 3D Printer Disadvantages
Noise: Most filament 3D printers have a noisy motion system, powered by buzzy stepper motors, although a few recent machines have quieter stepper drivers.
Mechanical complexity: The motion system on filament machines is relatively complex, involving belts, alignments and calibrations, and wear and tear.
Maintenance requirements: Because of the mechanical complexity, filament equipment tends to have more need for maintenance and repair.
Price: The price can also be a disadvantage: if you need a peculiar set of requirements, you might have to purchase a somewhat expensive device.
Layer lines: All filament machines suffer from relatively poor print surface quality due to the presence of “layer lines”. These can be fixed in post-processing, but that’s not always done.
Resin 3D Printers
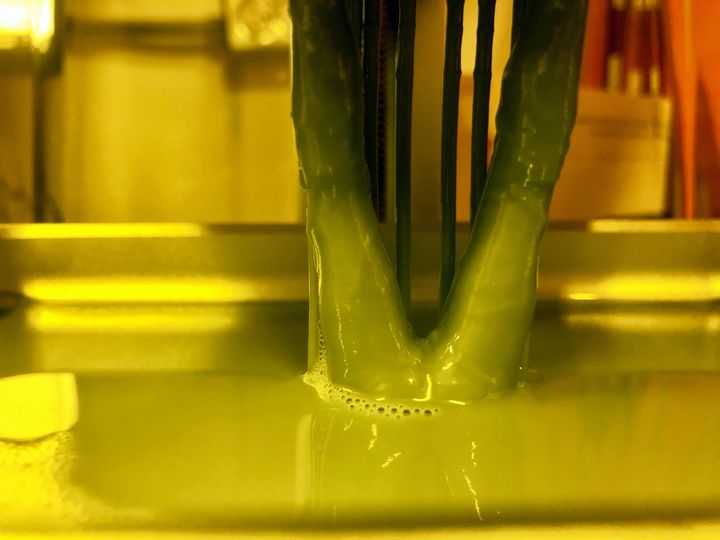

These machines are the relatively new among the desktop fleet, and have slightly less material choice than found with filament equipment. However, they are gaining in popularity and now occupy a significant portion of the market.
Resin 3D Printer Advantages
High resolution: The resolution of resin 3D printers can be quite a bit more than filament machines due to the size of the light engine’s pixels.
Surface quality: Surface quality is typically far better on resin 3D prints due to the nature of how the polymers fuse during printing.
Low maintenance: Having far fewer parts, resin 3D printers typically require a great deal less maintenance than filament 3D printers.
Quiet: Resin 3D printers are typically silent in operation.
Small footprint: Due to a small print volume, resin 3D printers typically take up only a small amount of desk space.
Exotic materials: Many exotic engineering materials are beginning to appear in the market, though many are only for filament equipment.
Resin 3D Printer Disadvantages
Small build volume: The print volumes are typically quite small, but suitable for high-resolution small parts.
Thermoset materials: The thermoset materials used in resin 3D printers cannot easily be recycled.
Limited materials choice: There are far fewer materials choices available for resin 3D printer operators, and limited engineering materials. Often you will see “ABS-like” resins, but they are not really ABS.
Durability: Resin 3D prints can break down, particularly if exposed to UV radiation outside.
Tank wear: The most common design for resin 3D printers requires relatively frequent replacement of the resin tank as it will slowly erode during printing.
IPA usage: Cleaning wet resin off a completed print requires the presence of a large tub of flammable IPA. Some installations may not want that risky material present.
Toxicity: Most 3D printer resins are toxic in liquid form, requiring PPE to handle, and they can emit noxious fumes that require ventilation. The dirty IPA must be disposed of using proper handling techniques.
Light engine burnout: The resin 3D printer’s light engines are used repeatedly, thousands of times, and some can eventually burn out, requiring replacement.
There you have it; the advantages and disadvantages of the two main types of desktop 3D printers.
It’s important to not simply pick one or the other based on a single factor, like maximum resolution or biggest print volume. That’s because when you make that choice, you get all the disadvantages along with the advantages and you must live with them. Be prepared for all of the above when you make your choice.
