
SPONSORED CONTENT
One tends to think of jewelry making as an art. It is quite challenging trying to fathom how two industrial techniques are used to create delicate jewelry. 3D printing is an additive process and CNC machining uses a subtractive technique, but both methods produce fine pieces.
Jewellery making processes
Design, building the master model, and investment casting (otherwise known as lost wax casting), are three stages of jewelry making. These processes can surely benefit from the advantages of rapid prototyping that is an integral component of additive and subtractive technologies. Companies such as 3D Hubs can vouch for their customers, who have accelerated their time-to-market speeds. This is due to rapid quote management, easy to upload CAD/CAM files, and instant Design for Manufacturing (DfM) feedback.
Jewellery production with CNC machining
One-off production is not typically seen as a practical approach in manufacturing. It is costly. However, in the world of jewelry production, custom jewelry is looked upon favorably. This is where CNC machining shines. Custom CNC machining is very competitive in terms of pricing. This is made possible by the fact that CNC machining is highly automated.
From beginning to end
The whole process, including post-processing, can be completed by the machine. The investment casting stage of jewelry making can be “cast away” by CNC milling. With the appropriate CAM design, CNC processing can emboss, engrave, texturize, and polish. Keep in mind that adjustments for different materials that may be less heat-resistant than metal, need to be made, but can be taken care of in the design. Undercutting, which is often required in bangles and earrings, is a little trickier with three- or four-axis machines. Five-axis machines manage undercutting just fine, but these machines are more expensive and can be slower.
Jewellery production with 3D printing
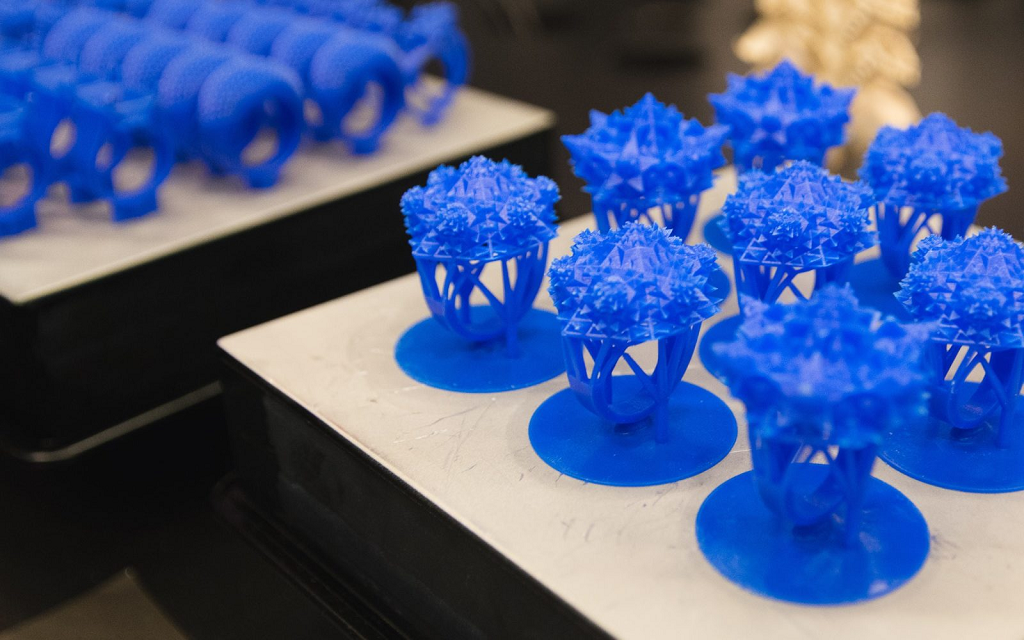
Creating jewellery with a 3D printer is excellent for runs that are longer, and for design diversity. Because the process is subtractive, undercutting can be easily achieved. For the jewelry maker, there are no design restrictions with 3D printing. 3D printing has made the labor-intensive task of investment casting, as simple as drizzling wax or resin onto a printer build plate. Molds can be produced with a number of design patterns on one mold, and in one run.

Why use 3D printing?
There are several advantages to using 3D printing to produce jewelry. These include:
- Very complex designs can be created. Historically, jewelry casting patterns were carved from wax using CNC machines. 3D printing is not restricted by the limitations of CNC machining and is able to produce parts that have in the past were impossible to make. Designs can also easily be customized.
- With 3D printing, multiple patterns can be made at once and within a very short time frame. This has significantly reduced lead times as well as cost when compared to traditional pattern making techniques (wax CNC, aluminum molds for casting etc).
- 3D printing also allows multiple designs to be produced in a single print. This means it is very cost competitive pricing for low production volumes (an important issue for jewelry where customers typically want a one-off piece).
Direct printing
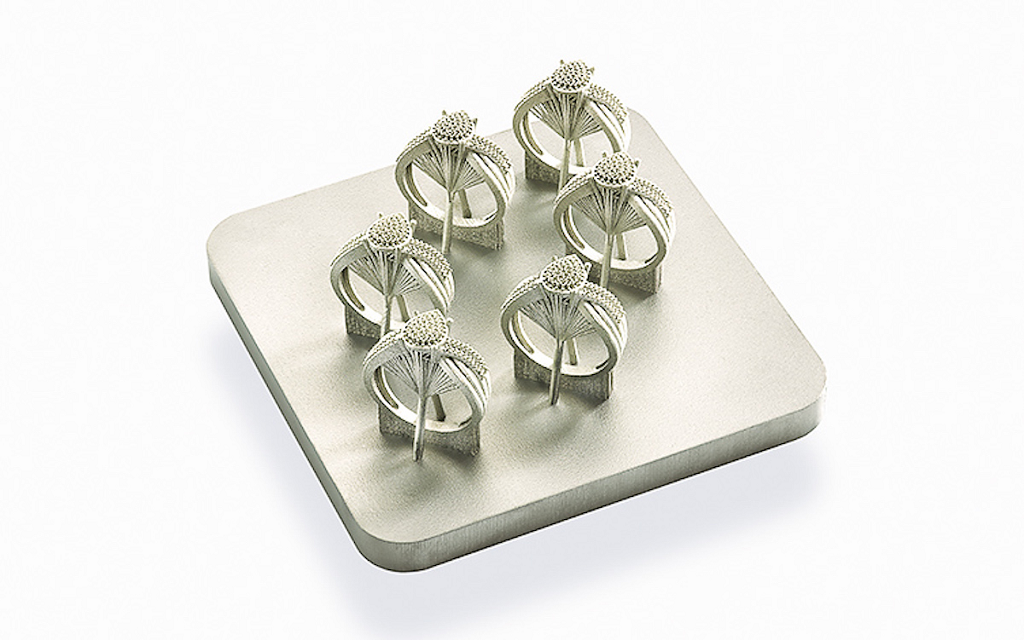
A much less popular method of producing jewelry via 3D printing is directly printing parts from metal powder. Parts are able to be printed via gold, silver or platinum alloys and then require a significant amount of post-processed to an appropriate finish. Direct printing of jewelry is generally more expensive than investment casting, even for one-off pieces, and requires a very high level of precious powder management. Use the 3d printing service of 3D Hubs to detect complex features in your models. You will instantly receive design optimisation suggestions to reduce the cost of manufacturing of your parts.
DMLS/SLM
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) or selective laser melting (SLM) are powder bed fusion techniques used for the production of metal parts. To accurately produce parts DMLS/SLM require a significant amount of support to be included on the part during printing. High temperatures result in high levels of stress meaning parts are often susceptible to warping or deformation. This leads to significant post-processing being needed to remove the support and finish the surface where it was attached.

Which 3D printing processes are suitable for jewellery making?
Stereolithography (SLA) and Direct Light Processing (DLP) are both excellent Vat Photopolymerization techniques used for pattern molding. The process builds up layers of uncured light-sensitive polymer resin, one layer at a time, at a height of 100 microns or less. The light source scans the resin, chemically solidifying it. SLA and DLP use different light sources: an ultraviolet light, and a digital projection screen, respectively. DLP is quicker but can be less accurate than SLA because of pixelization. 3D printing jewelry does require post-processing to complete the curing. However, this technology can completely dispose of any material residues when printing pattern molds.
Rules of thumb
- SLA/DLP offers a cost-effective method for producing jewelry patterns for investment casting however the designs require support material and a strict burnout procedure must be followed to ensure full burnout of the resin.
- DOD is capable of producing investment casting patterns at a higher level of detail and does not require the strict burnout procedures required for SLA/DLP resins however it is more expensive.
- Direct printing of metal jewelry is the most uncommon and expensive method for producing jewelry yet it offers the shortest production chain. Significant post-processing is required after the print is complete.
