What is the MFI and why does it matter for additive manufacturing?
Material selection is a crucial part of polymer 3D printing, especially when it scales to the high-speed, high-precision world of additive manufacturing (AM). There are many metrics for evaluating the quality of polymer materials for 3D printing, but the Melt Flow Index (MFI) is one that tends to be underappreciated.
Even when it’s not a sufficient indicator of material quality, it’s certainly a necessary one. For that reason, engineers working in polymer 3D printing or additive manufacturing would be well served to ensure they have a good understanding of MFI and how it impacts the quality of polymer 3D-printed parts.
What is Melt Flow Index?
Melt Flow Index is a measure of the ease with which a polymer, in a molten state, can be extruded through a specified orifice under standardized conditions of temperature and pressure. It is commonly expressed in grams per ten minutes (g/10 min) and serves as a critical indicator of a polymer’s flow characteristics during processing.
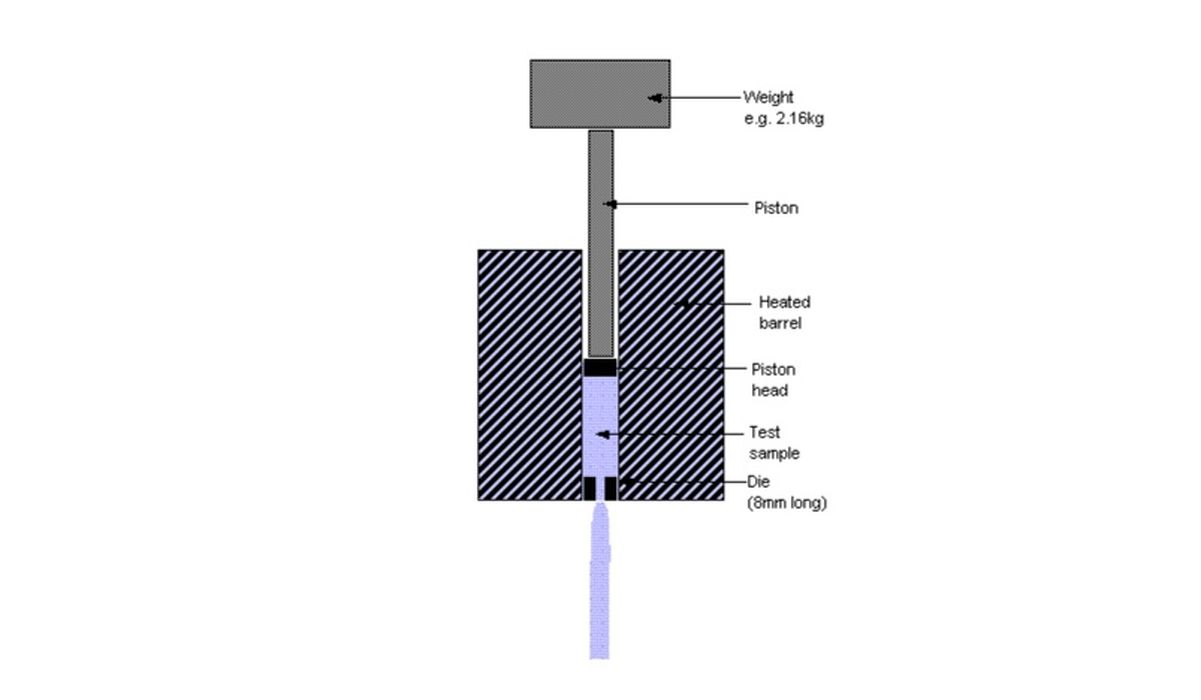
MFI and viscosity share an inverse relationship. A polymer with a low MFI has higher viscosity, indicating greater resistance to flow. Conversely, a high MFI corresponds to lower viscosity and better flow properties. The testing procedures for MFI are defined by international standards, such as ASTM D1238 and ISO 1133.
Why MFI Matters for 3D Printing
While most commonly used as a metric in molding, MFI’s applicability to polymer 3D printing is obvious. Melt flow directly influences how well a polymer can be extruded through the printer nozzle, thereby affecting layer adhesion, surface finish and overall print quality.
Understanding MFI can be beneficial to polymer 3D printing in many ways, including:
- Optimizing MFI to ensure a smooth and controlled material flow, reducing the risk of clogs or uneven extrusion.
- Polymers with higher MFI values generally exhibit better extrudability, allowing for faster and more efficient printing processes.
- Better control of the flow ensures precise deposition, resulting in accurate and detailed 3D-printed objects.
MFI is a crucial rheological parameter for 3D printing because it predicts how polymers behave when subjected to the temperatures and pressures of 3D printing processes. As a result, polymers with well-matched rheological properties, guided by MFI, can contribute to a smoother printing process and improved product quality.
How Melt Flow Affects Polymer 3D Printing
Polymers with higher melt flow rates generally exhibit better flowability, aiding in the creation of intricate and precise 3D-printed structures. MFI varies considerably among polymers, making different formulations more or less suitable for various applications.
Take these two types of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) filament as examples: Raise3D Premium and Raise3D Hyper Speed, where the latter’s MFI is roughly five times that of the former. Printing speed is the crucial factor here, as pointed out in a recent blog from Ember Prototypes, which found that flow can be a significant factor in reducing part strength at higher speeds as a result of under extrusion or inadequate flow.
Read the rest of this story at ENGINEERING.com
