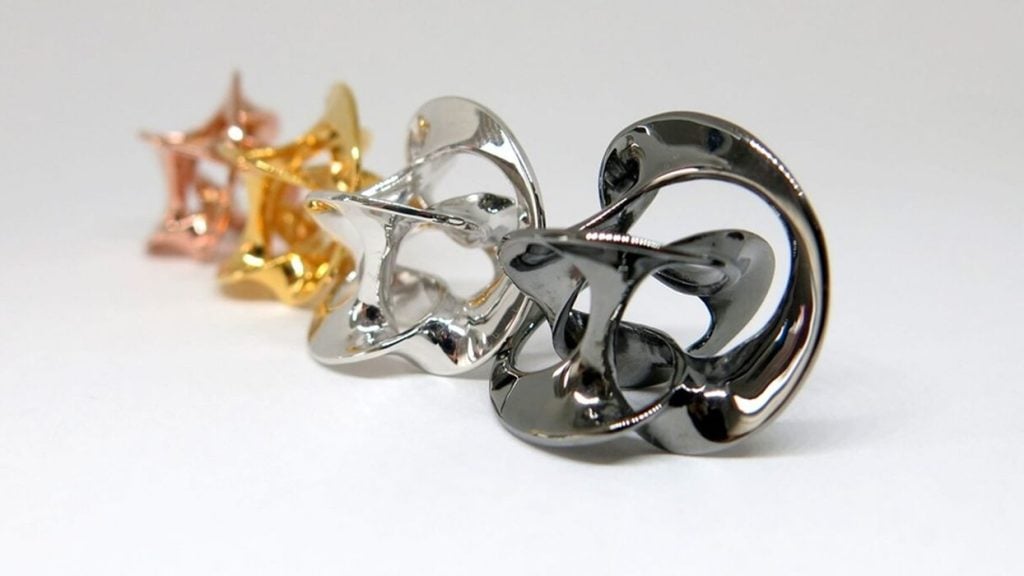
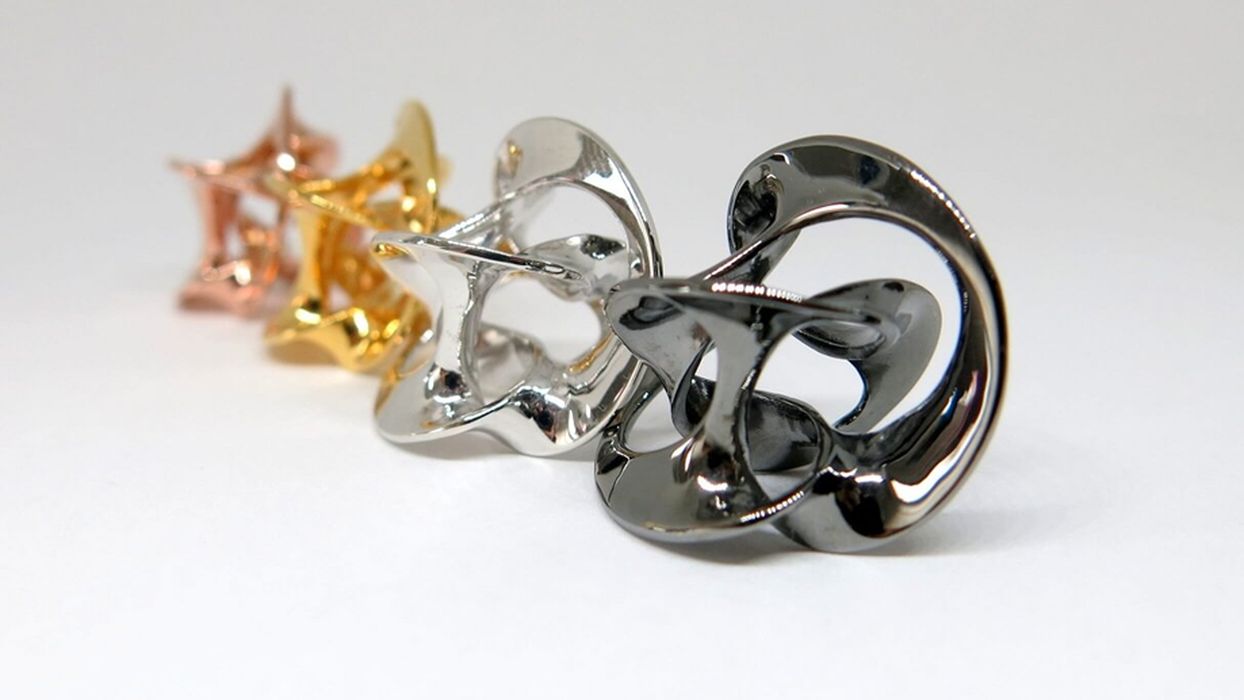
Charles R. Goulding and Andressa Bonafé look at the various ways 3D printing technology is being used to produce jewelry.
In recent years 3D printing has found numerous applications in the jewelry industry. In a recent article called “3D printed jewelry: Why you should start thinking about it?”, Sculpteo presents the top five reasons why additive manufacturing can be an asset in jewelry production:
Freedom of design: traditional technologies usually struggle or even fail to produce complex geometries and fine detail. 3D printing gives us the freedom to design abstract shapes and interlocking structures. In sum, anything you can imagine can be designed on a computer and then brought to life.
Lightweight pieces: heavy jewelry can be uncomfortable to wear or not practical. Lightweight 3D printing materials help overcome this issue, as do the use of lattice structures or hollowed pars.
High-quality, low cost: new 3D printing technology brings new levels of quality to jewelry design. Additive manufacturing is capable of reaching layer thickness of as little as 25 µm, which is 0.025 mm (thinner than the average hair thickness). New production techniques combine high quality and low cost.
Innovative materials: metal 3D printing allows for the production of designs in precious metals such as brass, bronze, or silver with different plating options. Plastic and resins are also interesting alternatives for certain items, with the added benefit of being strong, robust, and some even resistant to scratches.
3D printed jewelry molds: even those that do not wish to use additive manufacturing in their final product can take advantage of 3D printed molds using the lost wax process. Design and production processes can be made more efficient by the creation of master models that will later be used for mold making.
Efficiency and sustainability in jewelry design
Going beyond the aspects listed above, 3D printing can be an ally in fostering sustainability. A recent report by Positive Luxury points out that adherence to detailed traceability and transparency protocols has a growing impact on demand. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations are expected to influence one-third of all fine jewelry purchases by 2025.
Cloud Factory illustrates the great potential of using 3D metal printing to mass manufacture fine jewelry in a cost-effective and sustainable way. The Estonia-based company helps musicians, brands, and celebrities create bespoke jewelry merchandise through a fully managed service that offers concept building, manufacturing, branded packaging, and drop shipping. Its production method uses 3D metal printing which minimizes the usual cost, time, and waste to produce fine quality jewelry.
By combining green tech and resource-efficient 3D printing, Cloud Factory aims to change the face of a traditionally highly pollutive industry. Only natural and sustainable materials and 100% recycled precious metals are used in the process of making the 3D printed jewelry, through an on-demand manufacturing model. Production processes don’t require molding or casting but consist instead of 3D printing the jewelry item directly from 925 Sterling Silver powder, thereby using fewer resources compared to traditional manufacturing and also creating nearly zero waste.
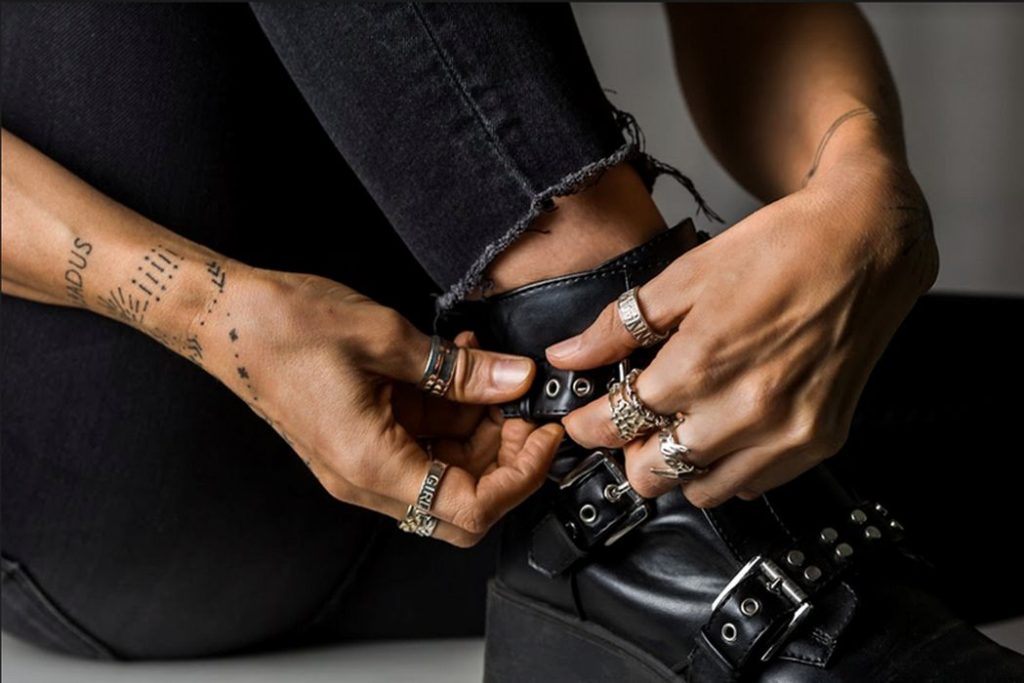

The fully managed service gives celebrities, brands, and creators the flexibility of offering fans quality state-of-the-art products without the time-consuming effort of having to develop and launch new products. Cloud Factory also broadens the possibilities for fan merchandise. The flexible 3D printing process allows clients to launch products quickly and adjust merchandising selections according to new content and fast-changing trends. It additionally gives fans a wider and more exclusive choice of memorabilia beyond the standard offerings, such as t-shirts, keyrings, and mugs.
Having recently raised a US$2.1M seed round, Cloud Factory is also looking to bridge the gap between digital and tangible jewelry products. The company plans to launch its first jewelry NFTs in collaboration with several global celebrities.
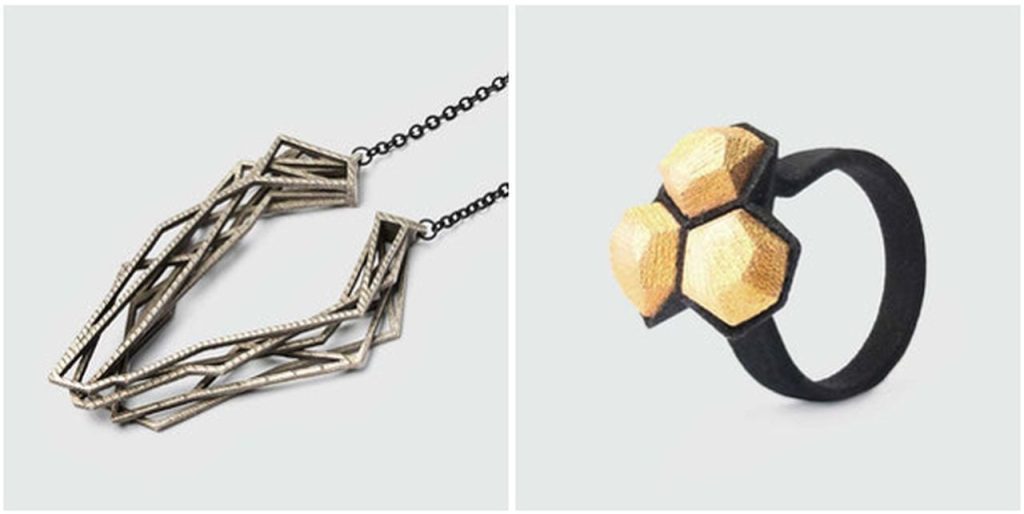

Other interesting examples from around the globe include Berlin-based RADIAN, a brand that aims to unite sustainability and contemporary crafting. Found in international boutiques, concept stores, and museum shops, RADIAN pieces illustrate how 3D printing as a production method opens up a new world of shapes and aesthetics. It allows not only for the use of innovative materials but also the creation of unique and artistic statement pieces.
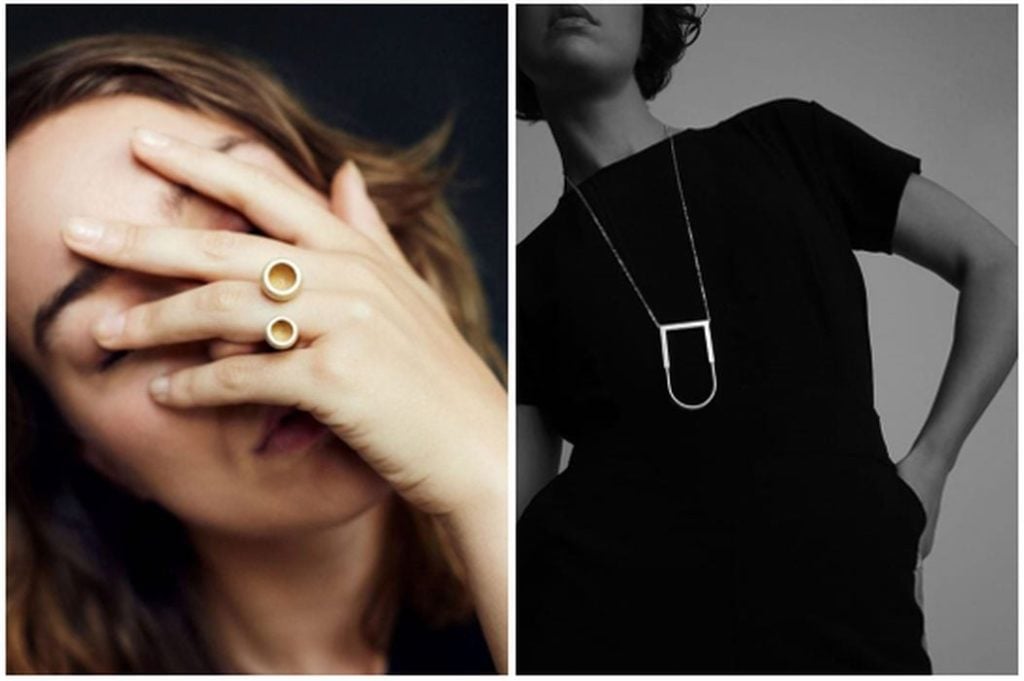

In New Zealand, HI Jewelry (short for Human Interface Jewelry) is committed to exploring the capabilities of the latest 3D printing methods and printers. The company creates innovative, personalized jewelry that combines human-centered design, advanced technology, and respect for the environment. Similarly, Belgian-based OLA uses additive manufacturing to blend elements of modern and minimalist design. OLA pieces are printed from polyamide nylon and stainless-steel powder, one layer at a time until completely formed. The nylon is colored and treated with a protective finish, while the steel jewelry is polished and plated with a layer of silver or gold.
3D Printed Jewelry in the US
In addition to the many advantages of 3D printing listed above, US-based jewelry designers and manufacturers can benefit from a Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit opportunity.
The now permanent R&D Tax Credit is available for companies developing new or improved products, processes and/or software.
3D printing can help boost a company’s R&D Tax Credits. Wages for technical employees creating, testing and revising 3D printed prototypes can be included as a percentage of eligible time spent for the R&D Tax Credit. Similarly, when used as a method of improving a process, time spent integrating 3D printing hardware and software counts as an eligible activity. Lastly, when used for modeling and preproduction, the costs of filaments consumed during the development process may also be recovered.
Whether it is used for creating and testing prototypes or for final production, 3D printing is a great indicator that R&D Credit eligible activities are taking place. Companies implementing this technology at any point should consider taking advantage of R&D Tax Credits.
Conclusion
A growing number of jewelry designers around the globe are using 3D printing to create innovative pieces while ensuring the sustainability and cost-efficiency of production processes. In the US, those applying additive manufacturing to jewelry design and production can take advantage of R&D tax credits to increase their chances of success in a highly competitive, ever-changing industry.

