
Recently, there has been a tremendous movement of Fortune 500 companies to invest in India’s digital infrastructure; Charles R. Goulding and Preeti Sulibhavi consider the implications of the 3D printing industry taking notice.
Since April 2020, over $30 billion, and counting, has been invested in India, largely due to the Reliance Jio platform, which is attracting top dollar for digital opportunities and Made in India electronics.
India holds the world’s second-highest population with 1.366 billion people as of 2019. With a burgeoning middle class and increasing demand for digital and electronic goods, India is witnessing a “digital renaissance,” so to speak.
Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited, d/b/a Jio, is an Indian telecommunications company and subsidiary of Jio Platforms, headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It operates a national LTE network with coverage across all 22 telecom circles. It does not offer 2G or 3G service, and instead uses only voice over LTE to provide voice service on its 4G network. Jio soft-launched in December 2015 with a beta for partners and employees, and became publicly available in September 2016. As of December 31, 2019, it is the largest mobile network operator in India and the third-largest mobile network operator in the world with over 387.5 million subscribers.
3D printing / additive manufacturing itself is a leading digital global technology that can affect so many lives globally. 3D printed digital tools and products can be eligible for economic tax benefits such as the Research and Development Tax Credit.
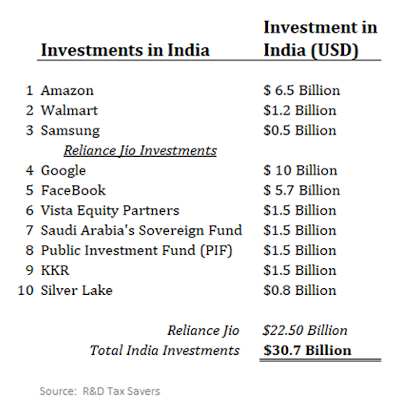
The above table presents tremendous new investments in digital technology that will enable India to leapfrog and connect its population.
3D printing and additive manufacturing activities can also produce economic benefits.
The Research and Development Tax Credit
Enacted in 1981, the now permanent Federal Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit allows a credit that typically ranges from 4%-7% of eligible spending for new and improved products and processes. Qualified research must meet the following four criteria:
- Must be technological in nature
- Must be a component of the taxpayer’s business
- Must represent R&D in the experimental sense and generally includes all such costs related to the development or improvement of a product or process
- Must eliminate uncertainty through a process of experimentation that considers one or more alternatives
Eligible costs include US employee wages, cost of supplies consumed in the R&D process, cost of pre-production testing, US contract research expenses, and certain costs associated with developing a patent.
On December 18, 2015, President Obama signed the PATH Act, making the R&D Tax Credit permanent. Beginning in 2016, the R&D credit has been used to offset Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) for companies with revenue below $50MM and, startup businesses can obtain up to $250,000 per year in payroll tax cash rebates.
Conclusion

We want to make sure that the 3D printing / additive manufacturing community understands the magnitude of these new investments in Indian digital technology.
