
Charles R. Goulding and Preeti Sulibhavi delve into Siemens’ groundbreaking announcement from Charlotte, showcasing the transformative potential of additive manufacturing in industrial automation.
In June 2024, Siemens made a groundbreaking announcement from their Charlotte, North Carolina location that has the potential to revolutionize industrial automation through the integration of additive manufacturing. This bold move highlights Siemens’ commitment to pushing the boundaries of technology and enhancing collaboration in the manufacturing sector.
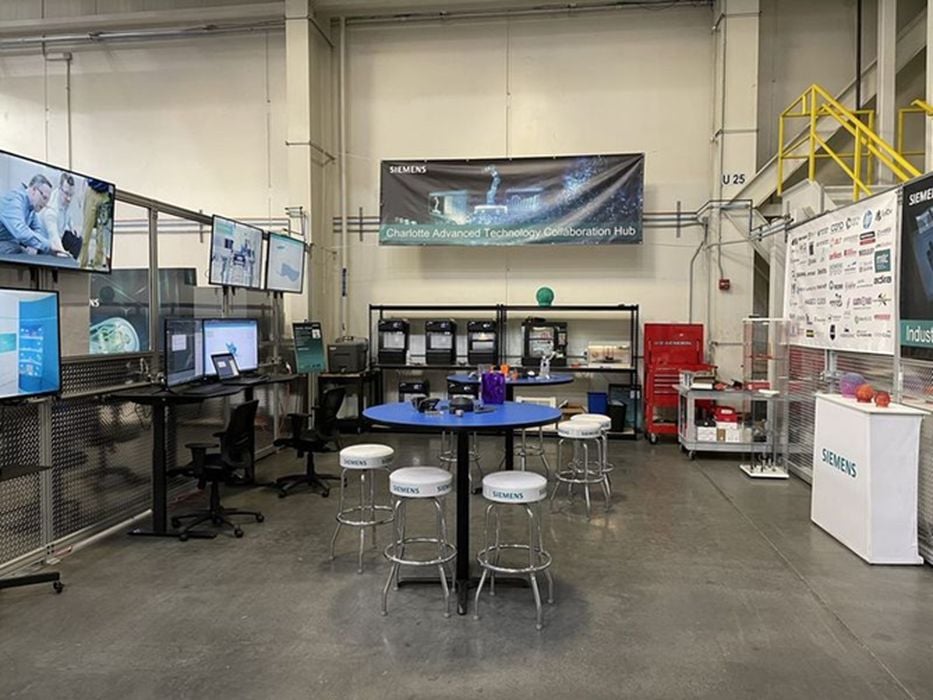
Siemens Charlotte: A Hub of Innovation
Charlotte, North Carolina, serves as the headquarters for Siemens’ Charlotte Advanced Technology Collaboration Hub (CATCH). This hub is a beacon of innovation, designed to foster collaboration among industry leaders, researchers, and technologists. The recent announcement underscores the pivotal role of collaboration in advancing industrial automation and additive manufacturing.
The New Program: A Collaborative Ecosystem
Central to Siemens’ new program is 3D printing, which forms the core of a comprehensive ecosystem integrating multiple additive technologies, digital manufacturing, digital twins, software, motion controls, CNC machines, and robots. This initiative aims to create a seamless and efficient manufacturing process, leveraging the strengths of various technologies and partners.
Key Players in Additive Manufacturing
Siemens‘ collaboration with prominent players in the additive manufacturing industry, such as Desktop Metal and ExOne, is a testament to their commitment to innovation. These partnerships enable Siemens to incorporate cutting-edge 3D printing technologies into their platform, enhancing the capabilities and efficiency of their manufacturing processes.
Desktop Metal and ExOne are at the forefront of 3D printing technology, offering advanced solutions that are now integrated into Siemens’ manufacturing ecosystem. This integration allows for the production of complex, high-quality components with unprecedented precision and speed.
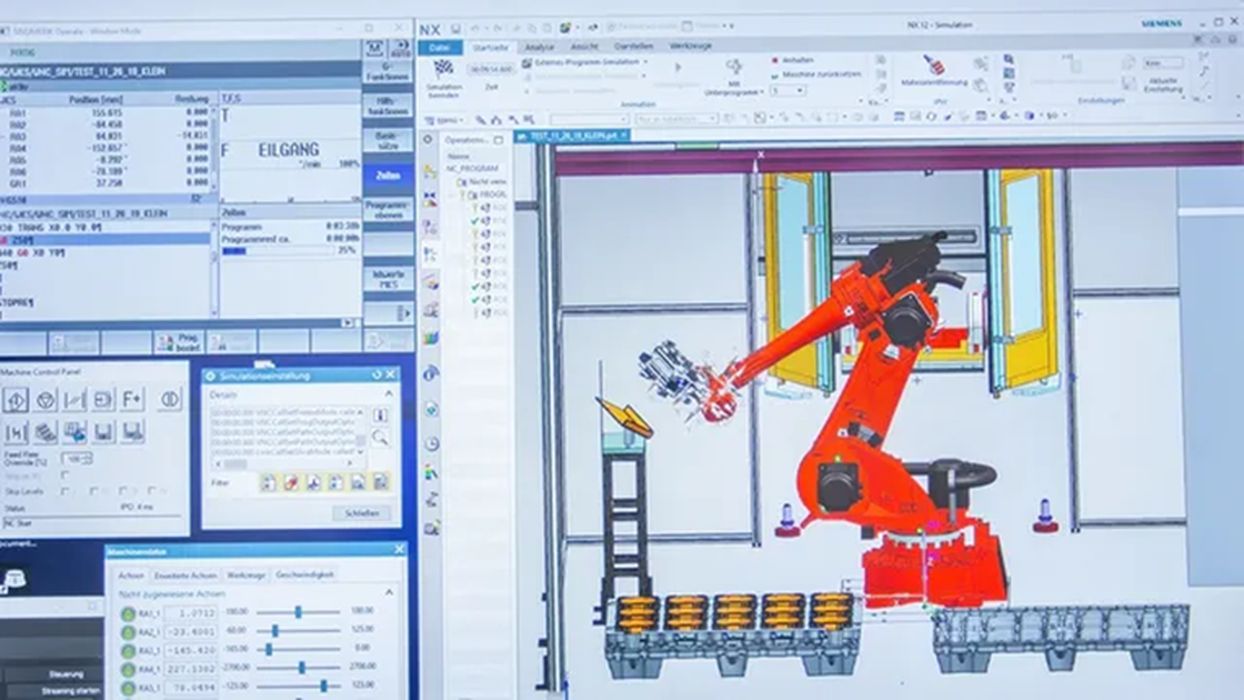
Advanced Robotics Integration
Robotics plays a crucial role in Siemens’ new program, with the Melito robot system and Siemens SINUMERIK RunMyRobot system being key components. These systems facilitate seamless integration between robots and CNC machines, streamlining the manufacturing process and increasing productivity.
Melito Robot System is known for its precision and versatility, the Melito robot system is designed to work in tandem with CNC machines, enhancing automation and reducing manual intervention.The SINUMERIK RunMyRobot System is an innovative system by Siemens that connects robots to CNC machines, enabling coordinated and efficient operation. This integration ensures that manufacturing processes are not only automated but also optimized for maximum efficiency.
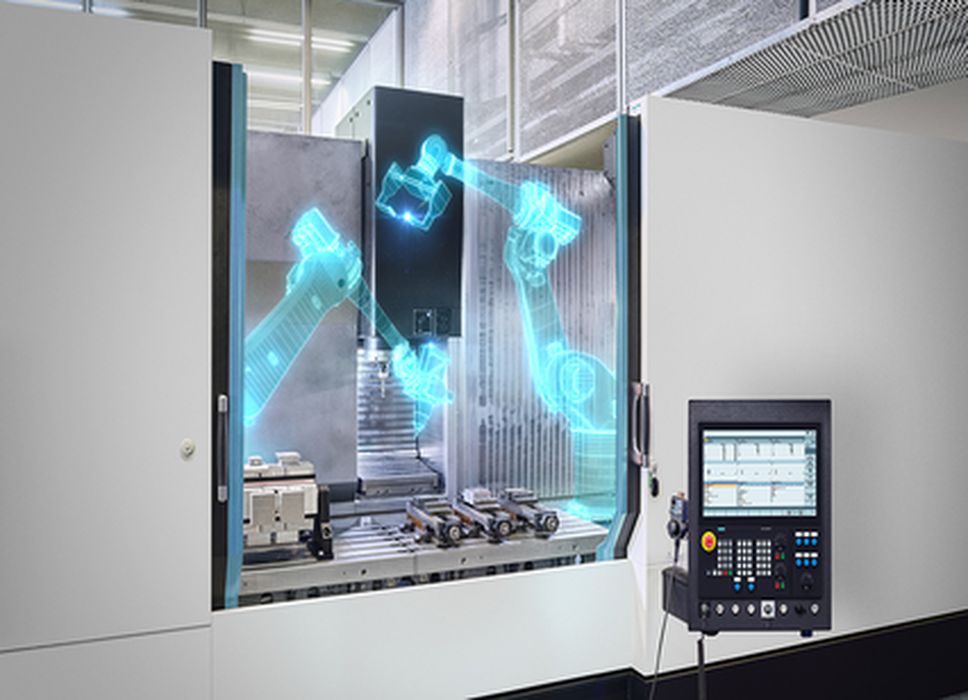

Collaboration with Industry Leaders
Siemens’ announcement is part of a broader trend of increased collaboration between industry leaders in the automation and manufacturing sectors. A notable example is the recent partnership between the Robert E. Morris Company, a leading U.S. machine tool integrator, and Stratasys, a pioneer in 3D printing technology.
This partnership exemplifies the growing trend of integrating CNC machines with 3D printing technology. By combining their expertise, the Robert E. Morris Company and Stratasys can offer comprehensive solutions that enhance the capabilities of both technologies.
Case Studies: Siemens’ 3D Printing Initiatives
Siemens has been actively involved in 3D printing across various locations in the United States, showcasing the practical applications and benefits of this technology.
In North Carolina, Siemens has implemented several 3D printing initiatives that highlight their commitment to innovation and efficiency. For instance, Siemens has used 3D printing to produce turbine blades for their energy sector, significantly reducing production time and costs while improving the performance of the turbines.
Siemens is a supplier of industrial controls for the safety elements of metal 3D printers. The Siemens SIRIUS 3SK product utilizes RFID technology for safety controls and has safety functions like EMERGENCY STOP and protective door monitoring implemented without programming up to SIL 3 and PL e.
Using 3D printing with Digital Twins: Before printing, designs must endure rigorous simulations of the printing process to mitigate risks, optimize the printing and improve yield. This method expands the full breadth of variables affecting the additive outcome, including the mixture of virgin and recycled print material, ambient humidity, machine parameters and more.
Implementing a comprehensive digital twin is essential to this process, including the initial simulation design, production and testing, to return additive manufacturing positively.
The digital twin is vital to construct and execute additive parts while managing delivery, manufacturing, operations and quality of manufacturing operations management. In addition, these components deliver awareness for harmonizing activities to provide accurate parts.
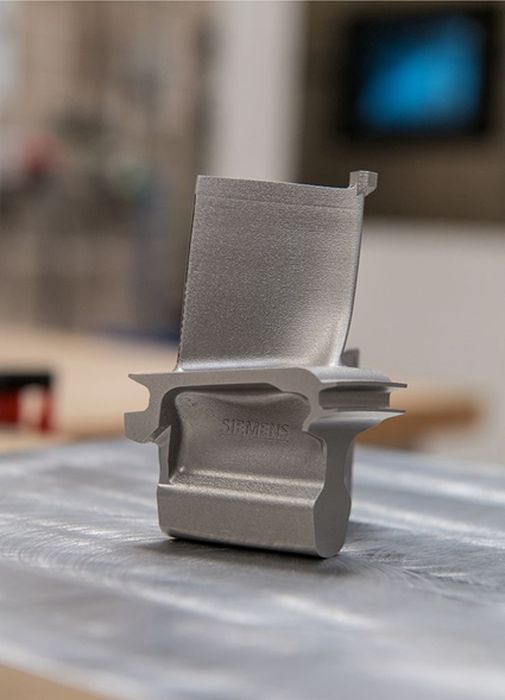

Beyond North Carolina, Siemens has also been leveraging 3D printing technology in other parts of the United States. In their Orlando, Florida facility, Siemens has established a state-of-the-art additive manufacturing laboratory that focuses on the production of high-performance components for the aerospace and energy industries.
Aerospace Components: Siemens uses 3D printing to produce critical components for aircraft engines, such as fuel nozzles and heat exchangers. These components benefit from the precision and customization offered by additive manufacturing, resulting in improved performance and durability of aerospace components.
Energy Sector Applications: Siemens’ additive manufacturing laboratory in Orlando also produces components for gas turbines and other energy-related applications. By utilizing 3D printing, Siemens is able to create parts with complex internal structures that enhance efficiency and reduce emissions.
The Power of Collaboration
The power of Siemens’ collaborative approach lies in its ability to offer customers a best-of-breed solution, as opposed to a single-vendor solution that may have weaker components. By partnering with industry leaders and integrating various advanced technologies, Siemens can provide comprehensive and optimized solutions that cater to the specific needs of their customers.
The Research & Development Tax Credit
The now permanent Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit is available for companies developing new or improved products, processes and/or software.
3D printing can help boost a company’s R&D Tax Credits. Wages for technical employees creating, testing and revising 3D printed prototypes can be included as a percentage of eligible time spent for the R&D Tax Credit. Similarly, when used as a method of improving a process, time spent integrating 3D printing hardware and software counts as an eligible activity. Lastly, when used for modeling and preproduction, the costs of filaments consumed during the development process may also be recovered.
Whether it is used for creating and testing prototypes or for final production, 3D printing is a great indicator that R&D Credit-eligible activities are taking place. Companies implementing this technology at any point should consider taking advantage of R&D Tax Credits.
Conclusion
Siemens’ recent announcement from their Charlotte hub marks a significant milestone in the integration of additive manufacturing and industrial automation. By placing 3D printing at the center of their collaborative ecosystem, Siemens is paving the way for a new era of manufacturing innovation. Through strategic partnerships and the incorporation of advanced technologies, Siemens can offer best-of-breed solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation across various industries.
As Siemens continues to push the boundaries of what is possible with 3D printing, the future of industrial automation looks brighter than ever. With their commitment to collaboration and innovation, Siemens is set to remain at the forefront of the manufacturing revolution, delivering cutting-edge solutions that meet the evolving needs of their customers.
