
Charles R. Goulding and Preeti Sulibhavi explore how leading HVAC companies are leveraging 3D printing, AI-driven cooling solutions, and federal incentives to drive sustainability, efficiency, and industry growth.
The Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) industry in the United States is experiencing a period of robust growth, driven by technological advancements and substantial federal incentives. A significant contributor to this evolution is the integration of 3D printing technologies, which are enhancing manufacturing processes and promoting sustainability. The Inflation Reduction Act has further bolstered the sector by providing considerable tax incentives to HVAC system designers, including architects, engineers, and mechanical contractors, encouraging innovation and energy efficiency.
Trane Technologies and the Yale Study on 3D Printing
Trane Technologies, a prominent player in the HVAC industry, has actively explored the benefits of additive manufacturing. In collaboration with the Yale School of the Environment and Desktop Metal, Trane participated in a comprehensive life-cycle assessment (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impact of binder jet 3D printing compared to traditional manufacturing methods. This study was commissioned by the Additive Manufacturer Green Trade Association (AMGTA), an organization dedicated to promoting sustainable practices in additive manufacturing.
The LCA focused on producing a steel scroll set used in Trane’s HVAC systems. The findings revealed a 38% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions when utilizing binder jetting over conventional casting methods. This significant decrease is primarily attributed to the reduced energy consumption during the production phase. Kevin Klug, Lead Additive Manufacturing Engineer for Trane Technologies, emphasized that these insights enable the company to consider additive manufacturing’s cost, productivity, and environmental impact earlier in the product design cycle, maximizing potential benefits.
The AMGTA, which sponsored this study, boasts an international membership comprising experts with extensive backgrounds in 3D printing and sustainability. The association’s Board of Directors includes leading providers and users of 3D printing technologies, underscoring its influential role in advancing sustainable additive manufacturing practices globally.
Carrier’s Commitment to Innovation and Sustainability
Carrier Global Corporation, credited with inventing the modern air conditioner in 1902, continues to lead in HVAC innovation. Demonstrating its commitment to sustainable solutions, Carrier completed the acquisition of Viessmann Climate Solutions in January 2024. This strategic move enhances Carrier’s portfolio with highly efficient and renewable climate solutions, leveraging Viessmann’s century-long record of innovation and sustainability. The integration of Viessmann’s 12,000 employees positions Carrier as a global leader in the rapidly growing residential and light commercial HVAC markets in Europe.
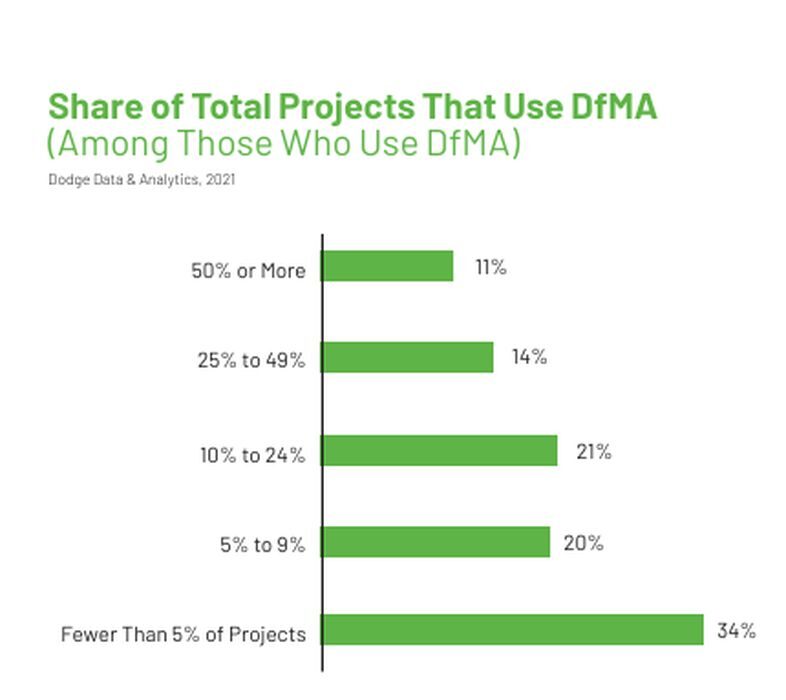
Analysts anticipate that this acquisition will bolster Carrier’s growth prospects, particularly in the heat pump segment. Despite initial sales lagging expectations, improved heating laws in Germany are expected to boost future orders. Additionally, Carrier’s focus on energy-efficient products aligns with the increasing demand driven by AI-related investments and onshoring trends. This includes Design for manufacturing and assembly (DfMA), which allows for offsite construction of building components with assembly onsite. As an approach, it is well documented to offer greater certainty in time and schedule, safer working conditions, and reduced waste.
Lennox International and Johnson Controls: Embracing 3D Printing
Lennox International has recognized the potential of 3D printing to enhance its manufacturing processes. By adopting additive manufacturing, Lennox aims to produce complex components with greater precision and reduced material waste, leading to more efficient and sustainable HVAC systems. This approach not only streamlines production but also allows for rapid prototyping and customization to meet diverse customer needs. Lennox is known for their very efficient roof top package units.
Johnson Controls and 3D Printing
Similarly, Johnson Controls has integrated 3D printing technologies into its operations. The company utilizes additive manufacturing to develop and test new HVAC components, accelerating the innovation cycle and improving product performance. By leveraging 3D printing, Johnson Controls can create intricate designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods, resulting in more efficient and reliable HVAC solutions.
Johnson owns York, a leading HVAC brand, and is known for its leading ESCO, or Energy Service Company, which retrofits large building campuses.
Johnson also operates the Warren Johnson Engineering Lab, which has 3D printers on site for various projects.
The Impact of AI Investments on the HVAC Industry
The HVAC industry is experiencing a surge in demand, partly due to substantial investments in artificial intelligence (AI). Data centers, which are critical for AI operations, require advanced cooling solutions to maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating. This necessity has led to increased demand for HVAC systems capable of efficiently managing the heat generated by extensive computational processes.
Companies like Ferguson, a major plumbing and HVAC supplier, are capitalizing on this trend. By providing state-of-the-art cooling systems tailored for data centers, Ferguson is addressing the unique challenges posed by AI infrastructure. This development not only drives growth within the HVAC sector but also encourages continuous innovation to meet the evolving needs of technology-driven environments.
The Research & Development Tax Credit
The now permanent Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit is available for companies developing new or improved products, processes and/or software.
3D printing can help boost a company’s R&D Tax Credits. Wages for technical employees creating, testing and revising 3D printed prototypes are typically eligible expenses toward the R&D Tax Credit. Similarly, when used as a method of improving a process, time spent integrating 3D printing hardware and software can also be an eligible R&D expense. Lastly, when used for modeling and preproduction, the costs of filaments consumed during the development process may also be recovered.
Whether it is used for creating and testing prototypes or for final production, 3D printing is a great indicator that R&D Credit-eligible activities are taking place. Companies implementing this technology at any point should consider taking advantage of R&D Tax Credits.
Conclusion
The U.S. HVAC industry stands at the intersection of tradition and innovation, with companies like Trane Technologies, Carrier Global Corporation, Lennox International, and Johnson Controls leading the way. The adoption of 3D printing technologies has revolutionized manufacturing processes, resulting in significant environmental benefits and operational efficiencies. Strategic acquisitions, such as Carrier’s integration of Viessmann Climate Solutions, underscore a commitment to sustainable and advanced climate solutions. Furthermore, the industry’s responsiveness to the demands of AI investments and data center cooling demonstrates its agility and forward-thinking approach. As these trends continue to evolve, the HVAC sector is well-positioned to deliver innovative, efficient, and environmentally responsible solutions for years to come.
