
The latest generation of engineering computers features new neural processing units (NPUs) to give AI a computational boost—but not all users will benefit equally.
Your computer may be personal, but that’s no longer enough. PCs are the latest convert in the spread of artificial intelligence (AI), and they’ve rebranded as AI PCs.
It’s not entirely a marketing buzzword. AI PCs, which are now being offered by major PC makers including Dell and Hewlett-Packard, have at least one new part to justify the new name: the neural processing unit, or NPU. Coexisting alongside the CPU—or integrated within it—and complementing the AI-friendly GPU, the NPU is meant to accelerate the machine learning calculations that are becoming increasingly important to modern software.
Engineering software is no exception. CAD and simulation providers have been testing the waters of AI, and it seems inevitable that it will play an increasingly prevalent role for engineers, architects and other professional users.
So, should engineers rush out to buy a new, NPU-equipped AI PC, or wait for the NPU to mature? Here’s what you need to know about the emerging tech and where it can make an impact.
CPU, GPU and NPU: The evolution of computing processors
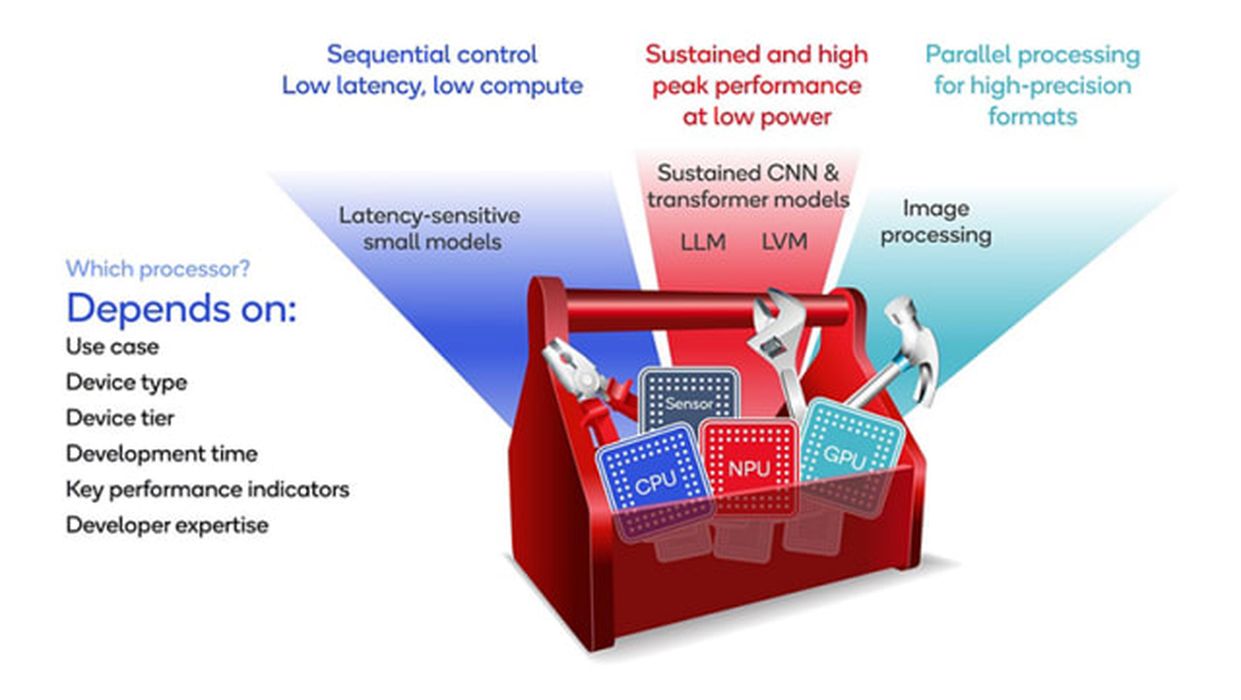
All computers are built around a central processing unit (CPU) that can handle a wide variety of instructions sequentially. Over time, CPU chips have become faster and more powerful. However, our appetite for crunching numbers grew and continues to grow even faster.
Chip designers responded by offloading specific CPU-intensive instructions, such as graphics and video rendering, to a second processor called a graphics processing unit (GPU). Through parallel processing, GPUs significantly improved the performance of graphics and computational tasks in demanding applications such as simulation and 3D rendering.
The recent advent of AI software dramatically increased the demand for processing data yet again. This time, chip designers have responded by offloading more CPU-intensive instructions, such as the mathematics for neural networks, to a third processor called a neural processing unit (NPU). The NPU specializes in AI computations such as matrix multiplication and convolution.
How do NPUs accelerate AI applications?
Unlike CPUs that sequentially process instructions, NPUs are optimized for parallel computing, making them highly efficient at machine learning algorithms, massive multimedia data transformation and neural network operations.
Read the rest of this story at ENGINEERING.com
