Charles R. Goulding and Ryan Donley look at the R&D spending of several major 3D print players.
It’s important to analyze the level of R&D occurring at the leading 3D printer manufacturers to understand the growth of the industry year over year. Both the technology and processes are expanding, touching every industry vertical.
Throughout 2021, revenue in the 3D printing industry reached US$10.6B and that number is expected by many sources to rise to over US$50B by 2030. We expect the trend in R&D spending to grow throughout the years as well. Innovation is the key to expansion in this industry and recent developments, such as bio-based material production and use in 3D printing, is accelerating the growth of manufacturing.
A table providing the past three years’ per capita R&D spend for eight companies is presented below:
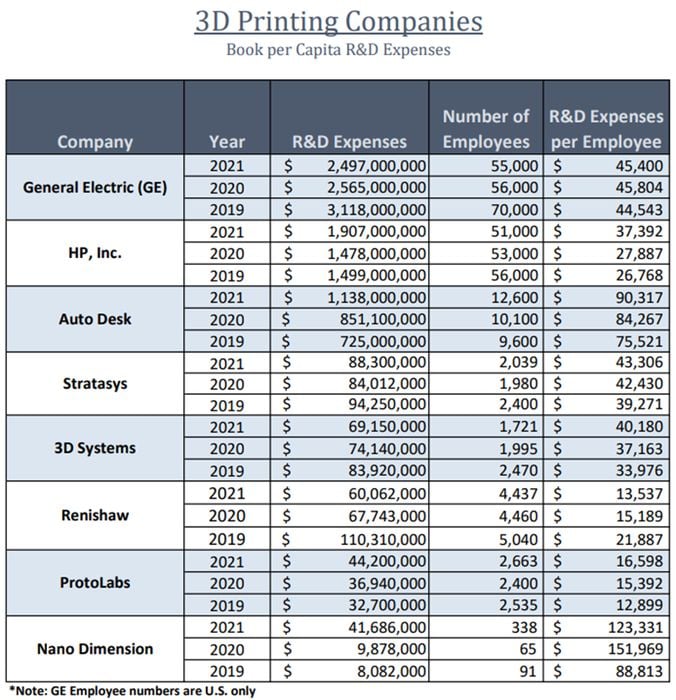
Some conclusions drawn from the four-company data for the pure-play 3D printers —Stratasys, 3D Systems, Protolabs (which also offers traditional manufacturing), and Nano Dimension — are as follows:
- This is an industry with a large commitment to R&D with three-year average spending of US$225M for these four 3D printing-focused companies.
- The pure 3D printer manufacturers are engineering/design-intensive since the average company per capita annual R&D spend is US$54,500 per employee; this excludes GE and HP.
- A significant percent change in average R&D spend (29.7%) occurred compared to 2020 due to growth in the industry.
- Nano Dimension is an electronics printing company, that topped the R&D Expense Per Capita table due to its small employee numbers and millions spent on R&D Expenditures.
- GE and HP Inc. are not 3D printing-specific, though they have committed large portions of R&D spending on 3D printing as the companies continue to grow their capabilities in this realm. Their large numbers skew the overall data results.
- After being private for several years, Desktop Metal, a specialty 3D printing systems company, went public in 2020. The company had total R&D expenditures of US$166M since publicly reporting. Desktop Metal also raised US$438M in venture funding from investors such as Google, BMW, and Ford.
- Since December 31st, 2021 Stratasys and 3D Systems have made important acquisitions that will presumably increase their prospective R&D annual expenses.
This table only reflects the R&D investment of large commercial 3D printer manufacturers. Other 3D printing or R&D investors include:
- Foreign, U.S. federal and local government
- Universities
- Software developers
- Material suppliers
- Designers and end-users
- Numerous privately-held 3D printer manufacturers, many of which have large R&D budgets, including Markforged (which recently went public) and Carbon
3D printing is accelerating quickly as the technology and processes become more sophisticated. Complex problems in manufacturing across numerous industries such as defense, automotive, and even medical technology are now seeing progressive solutions through advancements in 3D printing.