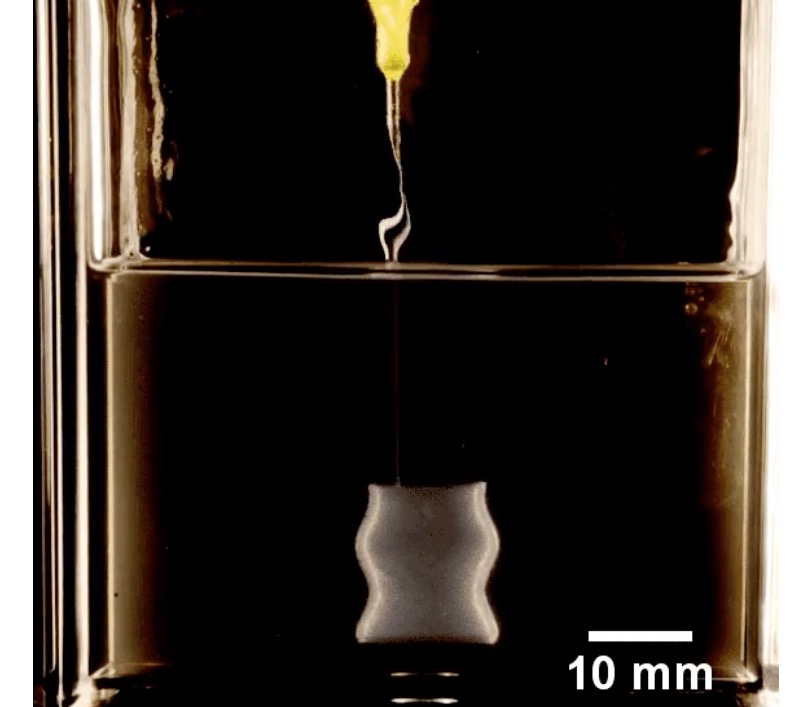
Researchers at the University of Florida have created a gel medium specifically for 3D printing medical implants.
This is a new take on a 3D bio printing process for living tissue, which up to now has been dominated by the “dissolvable scaffold” concept.
Dissolvable scaffolds are one way to overcome the problem of printing living cells: when deposited, they aren’t particularly attached to each other. They slop around, just like they do in the syringe before they are extruded.
The dissolvable scaffold involves 3D printing a second non-living, non-toxic material that does stick together. It forms a kind of “scaffold” on which the living cells can be deposited. Over time the cells multiply and form into viable tissue segments in the shape of the scaffold. Meanwhile, the scaffold eventually dissolves away, leaving just the living tissue.
In the new concept, a gel is used to hold the deposited material in 3D positions for a time sufficient for them to grow together.
We previously saw something similar to this in an experiment by MIT and Steelcase a few weeks ago, but the purpose of that work was to rapidly 3D print rudimentary furniture designs.
This work is different in that the gel medium is designed to hold medically implantable structures. In fact, the gel material is what’s called an “organogel”, made from “squishy, microscopic, chemical balls that are packed together in mineral oil”.
The gel enabled the researchers to 3D print very thin-walled flimsy structures, entirely suitable for implantation into patients. They need only be washed off and are ready for use.
Although it is not stated in the report I’m reading, I suspect a future enhancement could be to include nutrients of some form within the gel to enable living cells to be deposited in arbitrary shapes. It may be possible to circulate nutrients in the gel’s liquid component.
We’re definitely not 3D printing organs here, but this is still a notable improvement to the technology of medical implants.
Via The Verge